Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
To invoke Fabric User data function items (Preview) from a console application in Python, you can send HTTP requests to the function endpoint that needs to be executed. In this quickstart, you learn how to set up a Python app using Visual Studio Code.
Prerequisites
- Install Visual Studio Code.
- Download Python 3.1 on your local machine.
- Create a Microsoft Fabric account for free if you don't have one.
- Create a workspace.
- Create a user data functions item and publish it. Check these articles on how to create one in VS Code or how to create one in the portal. Publish the changes so the user data functions item is ready to be invoked.
Create a console application to invoke the function
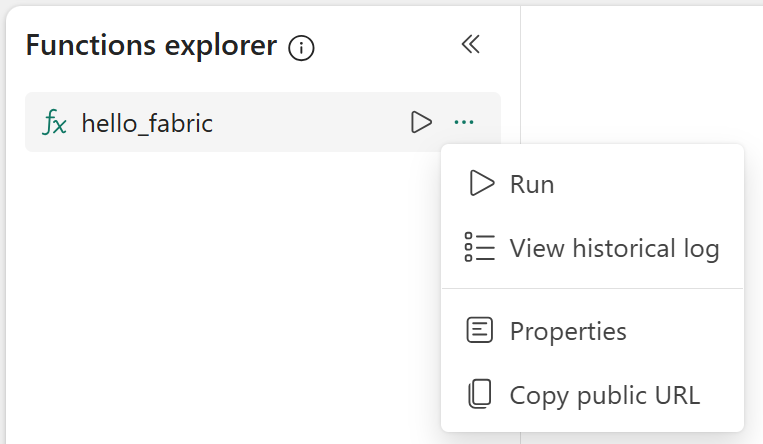
The function must be publicly accessible. In the Functions explorer, hover over the name of the function and select the ellipses icon (...) that appears, then select Properties. In the Properties pane that opens, enable Public access. You should also make a note of the Public URL to use in your Python application.
Create a new folder for your Python app, for example my-data-app. Open the folder in VS Code.
Set up the Python virtual environment in VS Code. To create local environments in VS Code, open the Command palette with Ctrl+Shift+P, then search for and select the Python: Create Environment command.
- The command presents a list of environment types and selects Venv.
- Select the Python interpreter version Python 3.11.
Run the following command to activate the virtual environment in the VS Code terminal.
venv\Scripts\activate.batNext, run the command to install the Python libraries needed for this example.
pip install azure-identity, requestsCreate an
app.pyfile and use the code to invoke the user data functions item.from azure.identity import InteractiveBrowserCredential import requests import json # Acquire a token # DO NOT USE IN PRODUCTION. # Below code to acquire token is to test the GraphQL endpoint and is for the purpose of development only. # For production, always register an application in a Microsoft Entra ID tenant and use the appropriate client_id and scopes. # https://learn.microsoft.com/fabric/data-engineering/connect-apps-api-graphql#create-a-microsoft-entra-app app = InteractiveBrowserCredential() scp = 'https://analysis.windows.net/powerbi/api/user_impersonation' result = app.get_token(scp) if not result.token: print('Error:', "Could not get access token") # Prepare headers headers = { 'Authorization': f'Bearer {result.token}', 'Content-Type': 'application/json' } FUNCTION_URL = '<REPLACE WITH USER DATA FUNCTION URL>' # Prepare the request data data = '{"name": "John"}' # JSON payload to send to the Azure Function headers = { # "Authorization": f"Bearer {access_token}", "Content-Type": "application/json" } try: # Call the user data function public URL response = requests.post(FUNCTION_URL, json=data, headers=headers) response.raise_for_status() print(json.dumps(response.json())) except Exception as e: print({"error": str(e)}, 500) if __name__ == "__main__": app.run(debug=True)Note
The example is for development purposes only. Update the application to use Microsoft Entra ID authentication before using the application for a production use case.
Invoking a function from an external application
Functions can be invoked by issuing a REST call to the endpoint URL. Select the function you want to invoke in the Functions explorer and select Copy Function URL. You can also turn on or off the ability to use this URL externally from the Properties menu.
Then, use this URL in your application to invoke the function. See Invoke user data functions from an application
Output schema
When invoking a User Data Function from an external application, the output schema will have the following format:
{
"functionName": "hello_fabric",
"invocationId": "1234567890",
"status": "Succeeded | BadRequest | Failed | Timeout | ResponseTooLarge",
"output": /*shows the result of the function dependeing on the output type*/,
"errors": [
{
"name": "Error name",
"message": "Error message",
"properties": {
/*Key value pairs custom to error*/
}
},
]
}
The following properties are returned:
- functionName: The name of the function that was executed.
- invocationId: The invocation ID for execution of a function.
- status: The outcome of the function's execution. This can have any of the following values:
Succeeded,BadRequest,Failed,TimeoutandResponseTooLarge. - output: The output value returned by the function.
- errors: If any errors were captured, this will return a list of each error with their name, error message and error properties.
Response codes
The function will return the following HTTP codes as a result of the execution.
| Response code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 OK (Success) | The request was successful |
| 403 (Forbidden) | The response was too large and the invocation failed. |
| 408 (Request Timeout) | The request failed due to the execution taking more than 200 seconds. |
| 409 (Conflict) | The request threw an exception during the execution. |
| 400 (Bad Request) | The request failed due to invalid or missing input parameters. |
| 500 (Internal Server Error) | The request failed due to an internal error. |
Debugging and testing
Debug the application in VS Code using python debugger. Add breakpoints if needed to debug if any issues. Learn more