Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this guide, we will create a new User Data Functions item and write new functions in it. Each User Data Functions item contains code that defines one or many functions that you can run individually.
Specifically, you learn how to:
- Create a user data functions item.
- Write a new function.
- Manage functions.
- Run your function.
Prerequisites
- A Microsoft Fabric capacity in one of the supported regions. If you don't have a Fabric capacity, you can create a trial capacity for free.
- A Fabric Workspace linked to that capacity
Create a new Fabric User Data Functions item
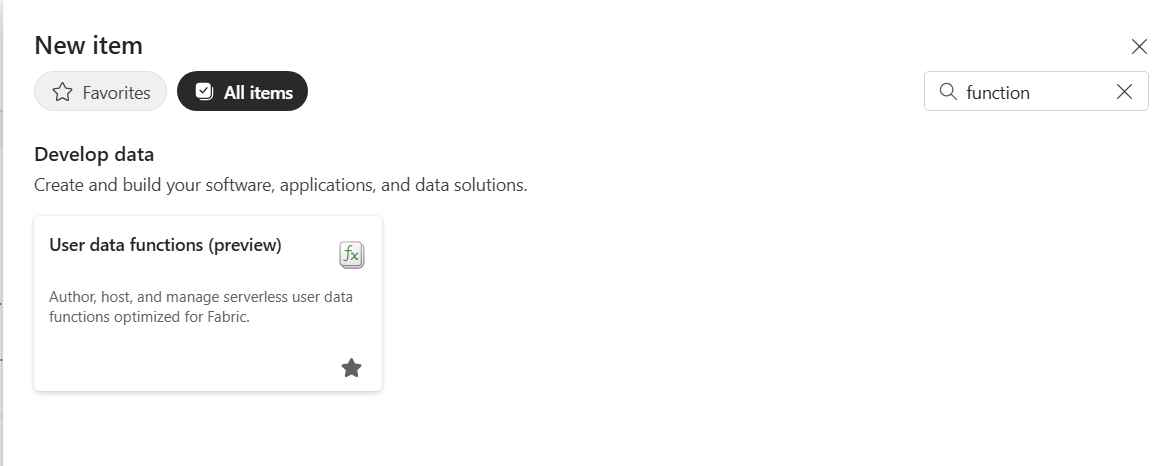
- Select your workspace, and select on + New item.
- Select Item type as All items. Search for and select User data functions.
Create a new user data functions item
In your workspace, select + New item.
In the pane that opens, search for
user data functions, then select the tile.Provide a Name for the user data functions item.
Select New function to create a
hello_fabricPython function template. The Functions explorer shows all the functions that are published and ready to be invoked.Once the
hello_fabricfunction is published, you can run it from the list of functions in the Functions explorer.
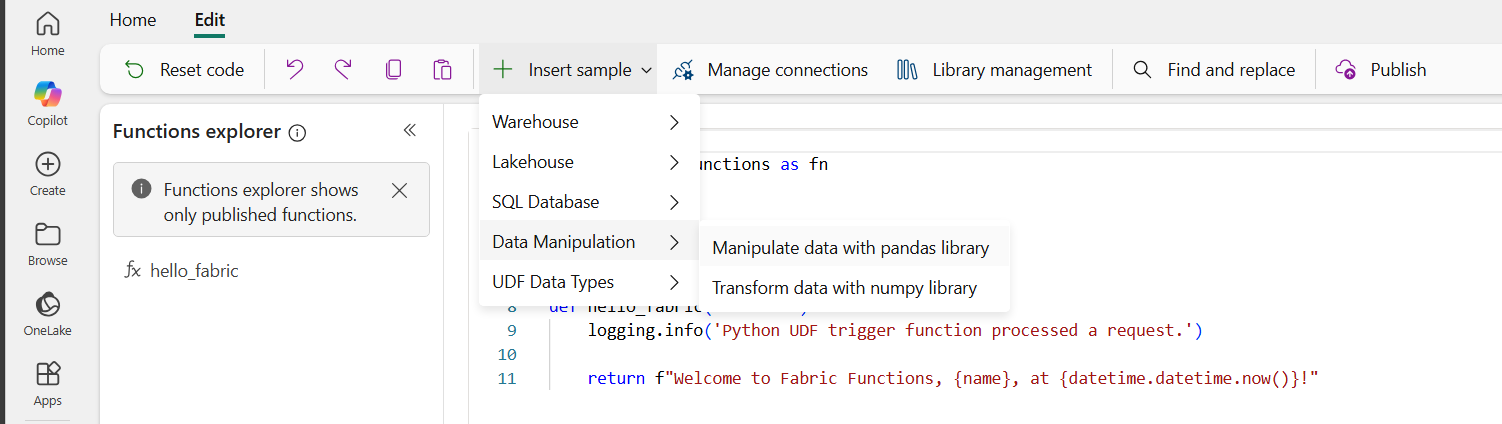
Add a new function from sample
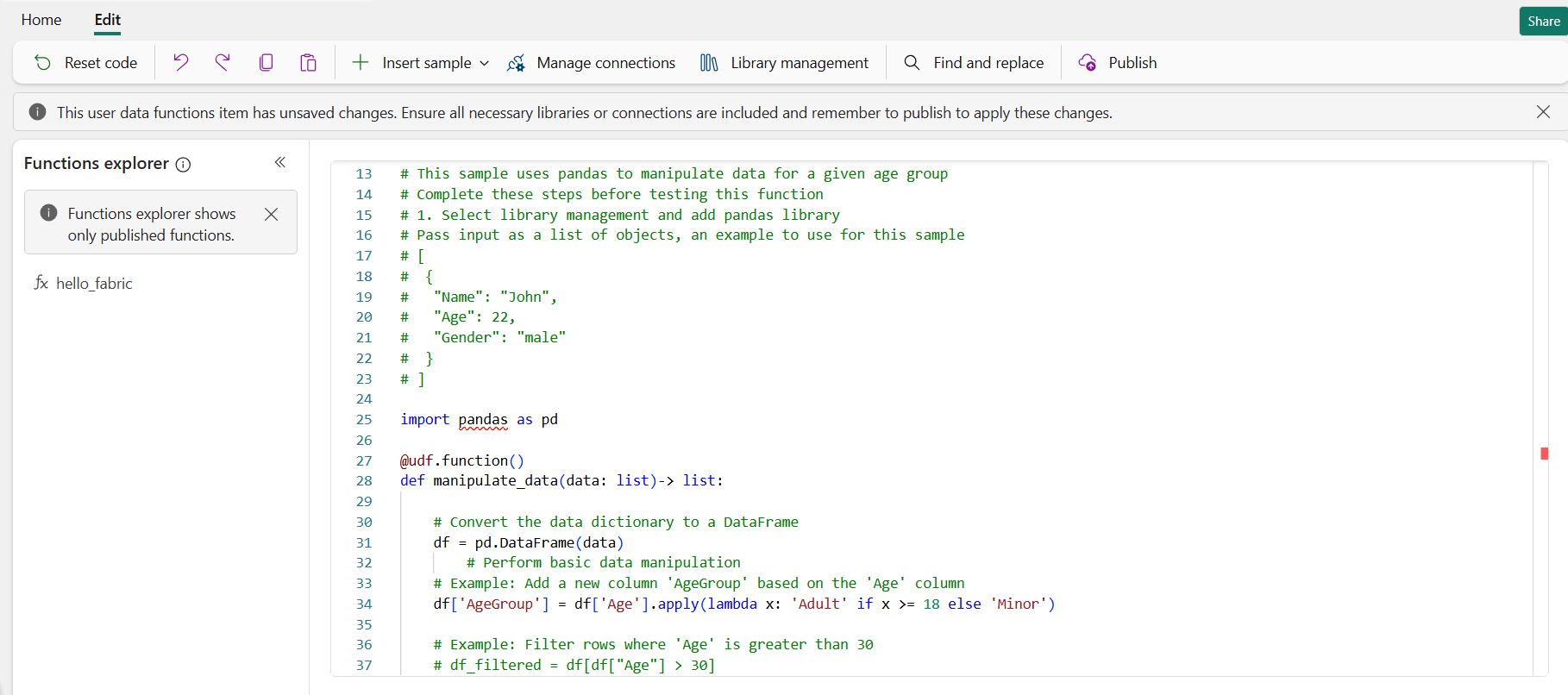
This is an example of how to add a new function from the Insert sample menu. In this case, we will add a function called Manipulate data with pandas library that uses the pandas library as a requirement. Follow the steps to add this sample function:
Select Library management to add the libraries that your function requires.
Note
fabric_user_data_functionslibrary is added by default and can't be removed. This library is required for the functionality of User data functions. You need to update the version of this library for any future releases of this SDK.Select pandas library and select the version. Once the library is added, it's automatically saved in your User Data Functions item.
Select Insert sample and select Manipulate data with pandas library. This action will insert sample code at the bottom of your code, after the other functions.
Once the sample is inserted into the editor, you can save your changes by selecting Publish. Publishing the changes may take a few minutes.
After the publish is completed, you will see the new function in the Functions explorer list. This function is now ready to be run from the portal, or invoked from another application or Fabric item, such as a data pipeline.
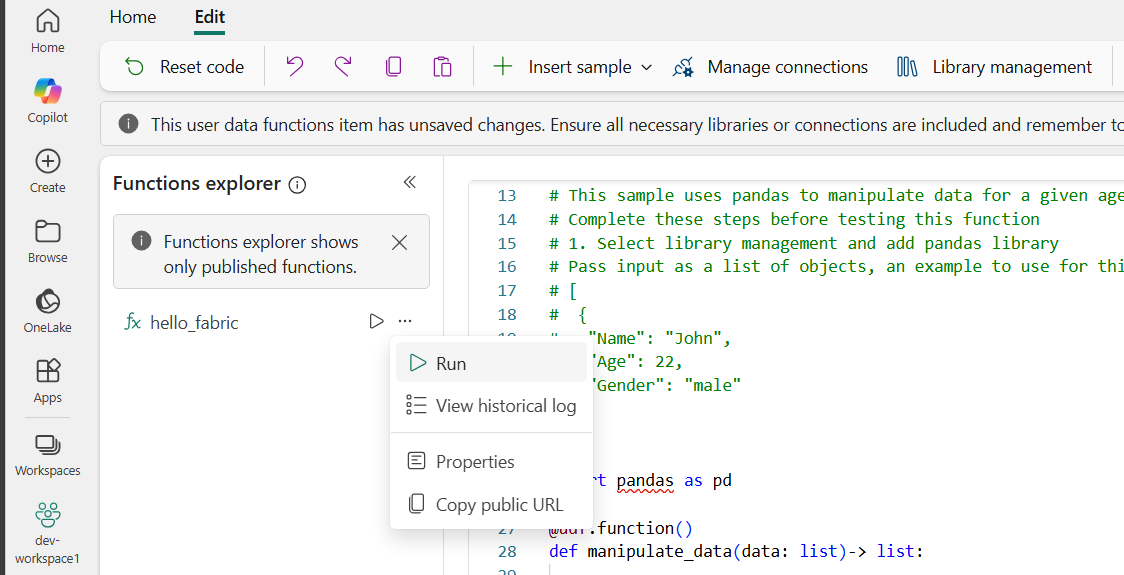
Run your function
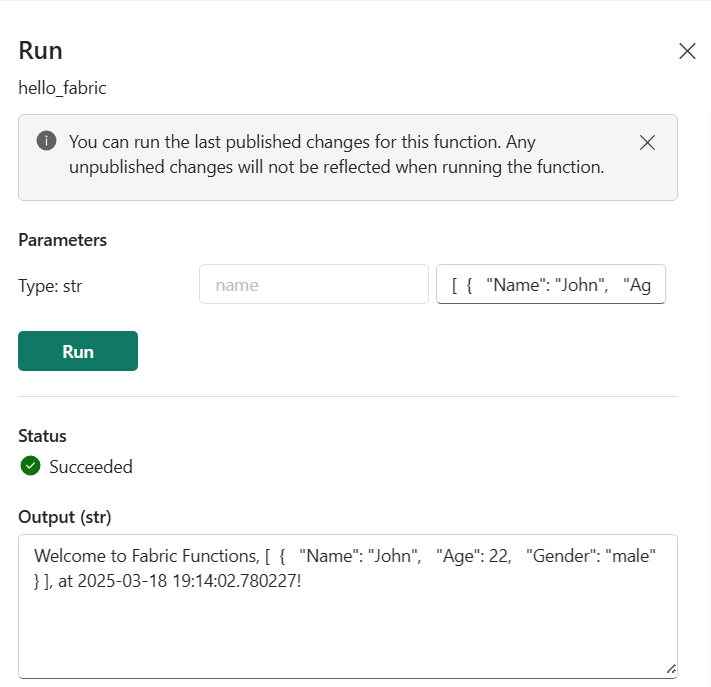
Select Run icon that shows up when you hover over a function in the Functions explorer list.
Pass the required parameters in presented as a form in the Functions explorer. In this case, we are going to run the
manipulate_datafunction which requires a JSON string as a parameter.[ { "Name": "John", "Age": 22, "Gender": "male" } ]Select Run to run the function.
You can see the live logs and the output for the function to validate if it ran successfully. Alternatively, you'll see an error message and logs from your function invocation.
Write a new function
Every runnable function starts with a @udf.function() decorator before the function definition. Read more about our Python Programming model. To write a new function, use the decorator @udf.function() at the beginning to declare it as a runnable function. Here's an example function:
# This sample allows you to pass a credit card number as an integer and mask it, leaving the last 4 digits.
@udf.function()
def maskCreditCard(cardNumber: int)-> str:
# Convert the card number to a string
cardNumberStr = str(cardNumber)
# Check if the card number is valid
if not cardNumber_str.isdigit() or not (13 <= len(cardNumber_str) <= 19):
raise ValueError("Invalid credit card number")
# Mask all but the last four digits
maskedNumber = '*' * (len(cardNumberStr) - 4) + cardNumber_str[-4:]
return str(maskedNumber)
Once the function is ready, publish the function to run it.
Programming model key concepts
Your User Data Functions use the User Data Functions Python Programming model to create, run, debug and modify individual functions. This is a first-party library that provides the necessary functionality to invoke your functions in Fabric and leverage all the integrations.
After creating your first function, the first lines of the code will contain the import statements with the necessary libraries to run your template.
import datetime
import fabric.functions as fn
import logging
udf = fn.UserDataFunctions()
Note
The import statement containing the fabric.functions library, and the line containing this statement udf = fn.UserDataFunctions() are necessary to run your functions properly. Your functions will not work properly if these lines are missing.
- To create, run, manage functions, you need
fabric.functionsSDK and few other important libraries such asloggingallows you to write custom logs. udf=fn.UserDataFunctions()is the construct to define functions within a User data functions item.
Manage data functions
Rename a function
Select into the code editor and update the name of the function. For example, rename
hello_fabrictohello_fabric1. Here's an example:@udf.function() def hello_fabric1(name: str) -> str: logging.info('Python UDF trigger function processed a request.') return f"Welcome to Fabric Functions, {name}, at {datetime.datetime.now()}!"After changing the name, select Publish to save these changes.
Once the changes are published, you can view the new name for the function in the Functions explorer.
Delete a function
To delete a function, select function code in the code editor and remove the entire code section. Publish the changes to delete it entirely from the user data functions item.
For example, to delete the hello_fabric function, remove the following code block:
@udf.function()
def hello_fabric(name: str) -> str:
logging.info('Python UDF trigger function processed a request.')
return f"Welcome to Fabric Functions, {name}, at {datetime.datetime.now()}!"
After the code is removed, you can select Publish to save your changes. Once the publish completes, you see an updated list of available functions in the Functions explorer.