Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article discusses how to disable debugging for ASP.NET applications running on .NET Framework.
Original product version: ASP.NET
Original KB number: 815157
Summary
ASP.NET supports compiling applications in a special debug mode that helps developer troubleshooting. Debug mode causes ASP.NET to compile applications with extra information. The information enables a debugger to closely monitor and control the execution of an application. Applications that are compiled in debug mode execute as expected. However, the performance of the application is affected. To avoid the effect on performance, it's a good idea to enable debugging only when a developer is doing interactive troubleshooting.
Debugging is disabled by default. Debugging is frequently enabled to troubleshoot a problem. But it's frequently not disabled after the problem is resolved. This article describes how to disable debugging for an ASP.NET application.
To disable debugging, modify the Web.config file or the Machine.config file, as detailed in the following sections.
Method 1: Modify the Web.config file
To disable debugging, add the compilation element to the Web.config file of the application by following these steps. The Web.config file is located in the application directory.
Open the Web.config file in a text editor, such as Notepad. The file is typically located in the application directory.
In the Web.config file, locate the compilation element. Debugging is enabled when the debug attribute in the compilation element is set to
true.Change the debug attribute to
falseto disable debugging for that application.The following code sample shows the compilation element with debug set to
false:<compilation debug="false"/>Save the Web.config file. The ASP.NET application automatically restarts.
Method 2: Modify the Machine.config file
You can also disable debugging for all applications on a system by modifying the Machine.config file. To confirm that debugging isn't enabled in the Machine.config file, follow these steps:
Open the Machine.config file in a text editor, such as Notepad. The file is typically located in the following folder:
%SystemRoot%\Microsoft.NET\Framework\%VersionNumber%\CONFIG\For 64-bit versions of the .NET Framework, the file is in the following folder:
%SystemRoot%\Microsoft.NET\Framework64\%VersionNumber%\CONFIG\In the Machine.config file, locate the compilation element. Debugging is enabled when the debug attribute in the compilation element is set to
true.If the debug attribute is
true, change the debug attribute tofalse.The following code sample shows the compilation element with debug set to
false:<compilation debug="false"/>Save the Machine.config file.
Method 3: Using IIS Manager (if the web application is hosted on IIS)
Open IIS Manager on the computer where the website is hosted (you can select Windows + R and type inetmgr):

Select the website or web application for which you want to enable or disable debug mode from the left-hand side tree view:
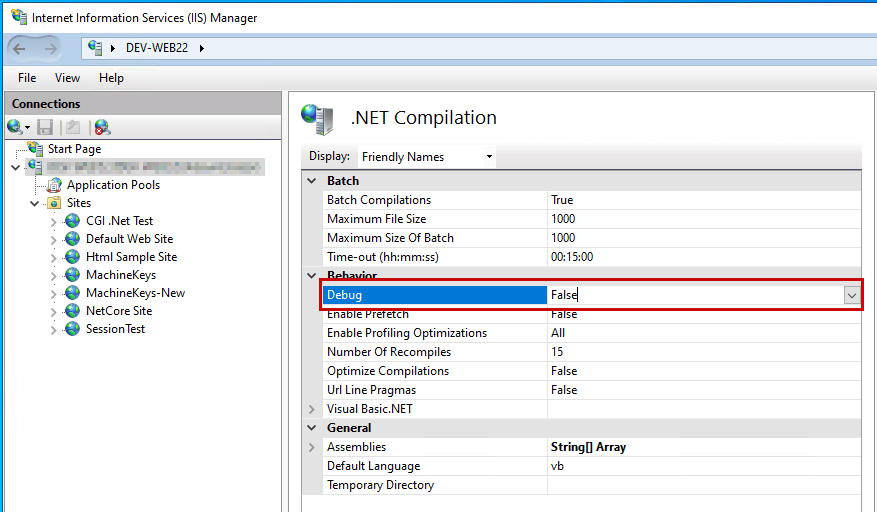
From the middle pane of IIS Manager, select the .NET Compilation icon:
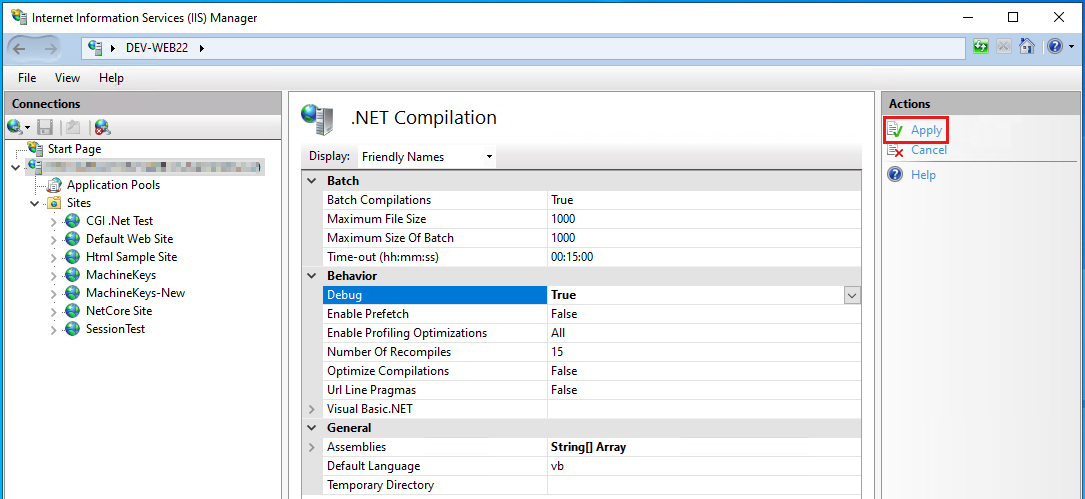
Within the list of parameter values displayed in the middle pane of IIS Manager, set the value of Debug under the Behavior category to:
- True: Enable debug mode.
- False: Disable debug mode.
Select the Apply button from the right-hand side pane of IIS Manager to save the changes to the IIS configuration: