Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Mirroring in Fabric provides an easy experience to avoid complex ETL (Extract Transform Load) and integrate your existing Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server estate with the rest of your data in Microsoft Fabric. You can continuously replicate your existing Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server directly into Fabric's OneLake. Inside Fabric, you can unlock powerful business intelligence, artificial intelligence, Data Engineering, Data Science, and data sharing scenarios.
For a tutorial on configuring your Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server for Mirroring in Fabric, see Tutorial: Configure Microsoft Fabric mirrored databases from Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server.
Why use Mirroring in Fabric?
With Mirroring in Fabric, you don't need to piece together different services from multiple vendors. Instead, you can enjoy a highly integrated, end-to-end, and easy-to-use product that is designed to simplify your analytics needs, and built for openness and collaboration between Microsoft, Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server, and the 1000s of technology solutions that can read the open-source Delta Lake table format.
What analytics experiences are built in?
Mirrored databases are an item in Fabric Data Warehousing distinct from the Warehouse and SQL analytics endpoint.
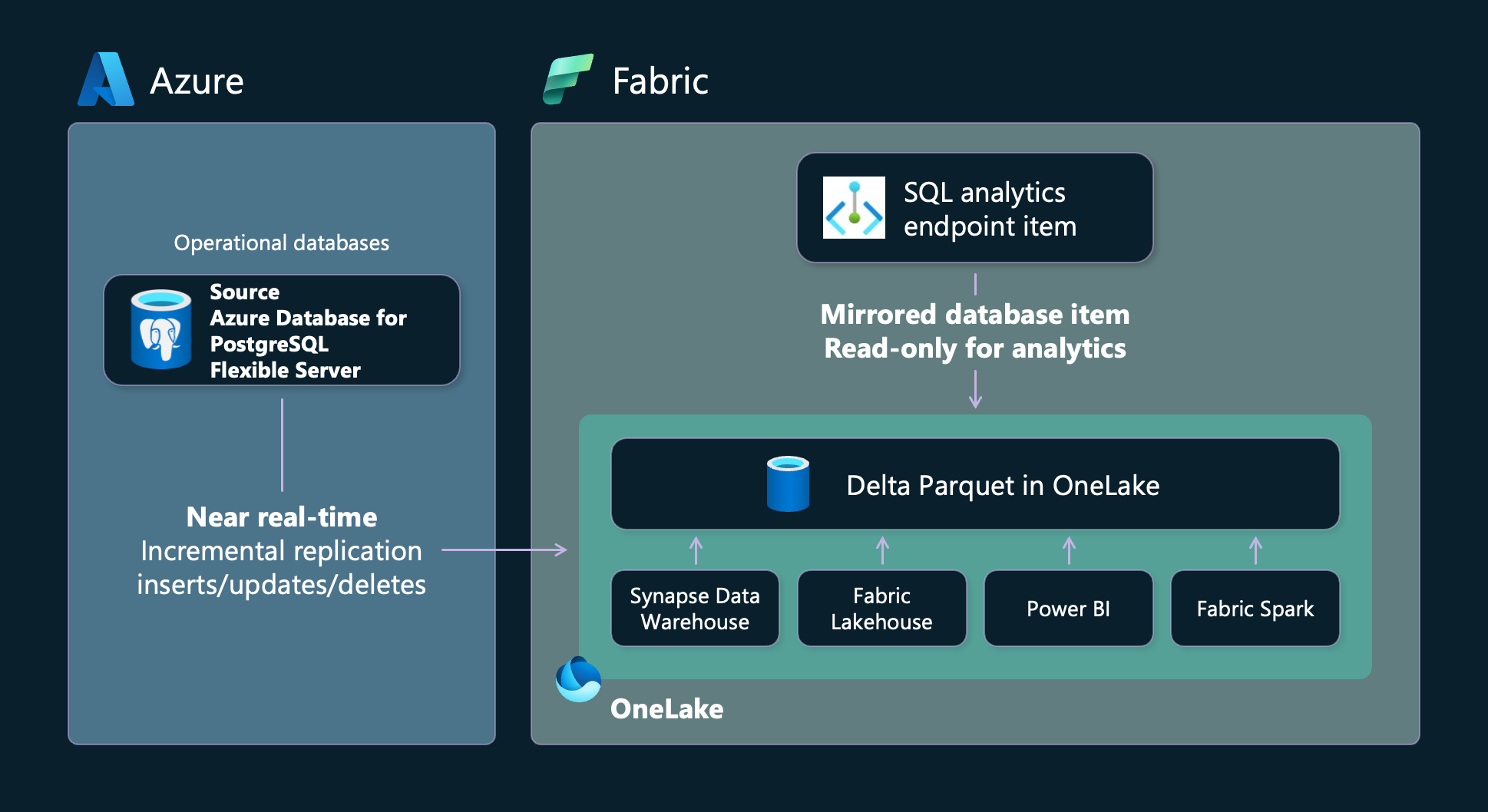
Mirroring creates three items in your Fabric workspace:
- The mirrored database item. Mirroring manages the replication of data into OneLake and conversion to Parquet, in an analytics-ready format. This enables downstream scenarios like data engineering, data science, and more.
- A SQL analytics endpoint
- A default semantic model
Each mirrored database in Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server has an autogenerated SQL analytics endpoint that provides a rich analytical experience on top of the Delta Tables created by the mirroring process. Users have access to familiar T-SQL commands that can define and query data objects but not manipulate the data from the SQL analytics endpoint, as it's a read-only copy. You can perform the following actions in the SQL analytics endpoint:
- Explore the tables that reference data in your Delta Lake tables from Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server.
- Create no code queries and views and explore data visually without writing a line of code.
- Develop SQL views, inline TVFs (Table-valued Functions), and stored procedures to encapsulate your semantics and business logic in T-SQL.
- Manage permissions on the objects.
- Query data in other Warehouses and Lakehouses in the same workspace.
In addition to the SQL query editor, there's a broad ecosystem of tooling that can query the SQL analytics endpoint, including SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), the mssql extension with Visual Studio Code, and even GitHub Copilot.
Network requirements
Currently, Mirroring doesn't support Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server behind an Azure Virtual Network or private networking. If you have your flexible server instance behind a private network, you can't enable Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server mirroring.
You need to update your Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server firewall rules to Allow public network access, and enable the Allow Azure services option to connect to your Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server.
Active transactions, workloads, and replicator engine behaviors
Active transactions continue to hold the write ahead log (WAL) truncation until the transaction commits and the mirrored Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server catches up, or the transaction aborts. Long-running transactions might result in the WAL filling up more than usual. WAL on source Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server should be monitored so that storage does not fill up. For more information, see WAL grows due to long-running transactions and CDC.
Each user workload varies. During initial snapshot, there might be more resource usage on the source database, for both CPU and IOPS (input/output operations per second, to read the pages). Table updates/delete operations can lead to increased log generation. Learn more on how to monitor resources for your Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server.
Compute tier support
The source Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server can be either a General Purpose or Memory Optimized compute tier. Burstable compute tier is not supported as source for mirroring.
To know more about compute tiers available in Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server, see Compute options in Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server.
Next step
Related content
- How to: Secure data Microsoft Fabric mirrored databases from Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server
- Limitations in Microsoft Fabric mirrored databases from Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server
- Monitor Fabric mirrored database replication
- Troubleshoot Fabric mirrored databases from Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server