Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article describes how to use Git integration and deployment pipelines for environments in Microsoft Fabric.
Integrate Git for Fabric environments
Fabric supports Git integration. Developers can use Git to back up, control versions, revert to previous stages, and collaborate on their work by using Git branches.
Important
This feature is in preview.
- Currently, Git supports only libraries and Spark compute, including Spark runtime.
- Git integration manages the staging state of the environment. To apply changes made in Git to the environment, they must be published. We recommend that you publish after you update the environment from Git to ensure the effectiveness of the configuration. You can use the Publish API of the environment to publish changes through the REST API if you prefer the code-first experience.
- The attached custom pool persists in an environment when you sync from a repo to a Fabric workspace. The pool definition is in the workspace setting. Cross-workspace referencing of the pool isn't supported. You must manually update instance_pool_id to an existing custom pool in your destination workspace space or revert to a starter pool by removing this property. For the full list of available pools in the destination workspace by the REST API, see Custom Pools - List Workspace Custom Pools. To create a new custom pool, see Custom Pools - Create Workspace Custom Pool.
- Each commit has an upper limit of 150 MB. Currently, custom libraries larger than 150 MB aren't supported through Git.
Connect the Fabric workspace to an Azure DevOps repository
If you're the admin of a workspace, go to Workspace settings and set up the connection in the Source control section. To learn more, see Manage a workspace with Git.
After you connect, you can find items, including the environments that are syncing with the repo.
Local representation of an environment in Git
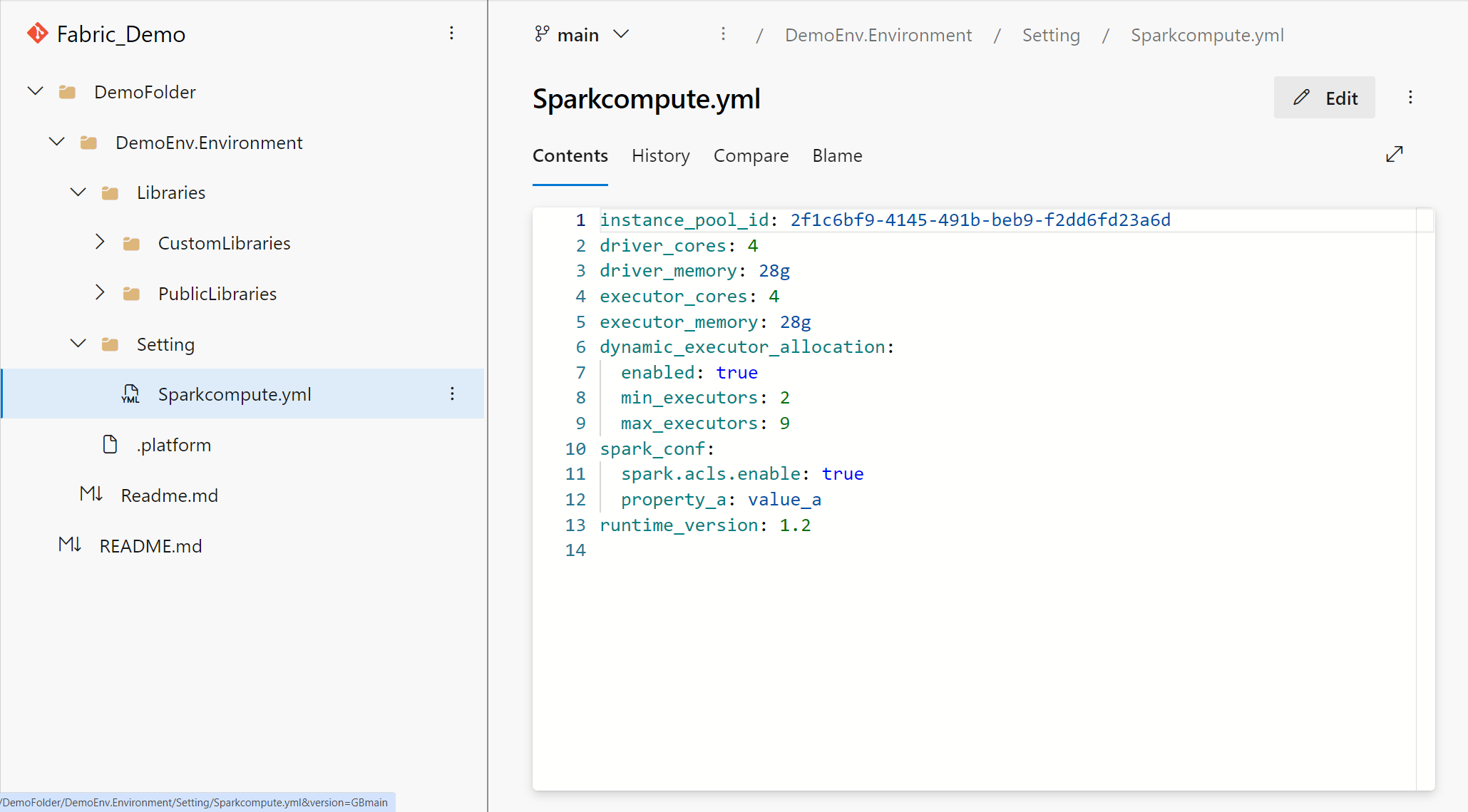
In the item root folder, environments are organized with a Libraries folder that contains PublicLibraries and CustomLibraries subfolders, along with the Setting folder.

Libraries
When you commit an environment to Git, the public library section is transformed into its YAML representation. The custom library is also committed along with its source file.

You can update the public library by editing the YAML representation. Just like the portal experience, you can specify a library from PyPI and Conda. You can specify the library with the expected version, a version range, or without a version. The system can help you determine a version that's compatible with other dependencies in your environment. To clear all the existing public libraries, delete the YAML file.
You can update the custom library by adding new files or deleting existing files directly.
Note
You can bring your own YAML file to manage the public library. The file name needs to be environment.yml so that the system can recognize it correctly.
Spark compute
The Spark compute section is also transformed into the YAML representation. Within this YAML file, you can switch the attached pool, fine-tune compute configurations, manage Spark properties, and select the Spark runtime that you want.
Set up a deployment pipeline for an environment
Important
This feature is in preview.
Fabric deployment pipelines simplify the process of delivering modified content across different phases, such as moving from development to test. The automatic pipeline can include the environment items to stream the re-creation process.
You can set up a deployment pipeline by assigning the workspaces with different phases. For more information, see Get started with deployment pipelines.
You can find the deploying status after you set up the pipeline successfully. After you select Deploy with the environment selected, all contents of the environment are deployed to the destination workspaces. The status of the original environment is preserved in this process so that the published configurations stay in the published state and require no extra publishing.
Important
Currently, the custom pool isn't supported in deployment pipelines. If the environment selects the custom pool, the configurations of the Compute section in the destination environment are set with default values. In this case, the environments keep showing diff in the deployment pipeline even if the deployment is done successfully.
Using deployment rules to specify different pools in a new workspace will be included in an upcoming release.