Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Get started with GitHub Copilot for Azure Preview to streamline your development workflow and enhance your productivity on the Azure platform. This guide walks you through the prerequisites and installation of the GitHub Copilot for Azure extension in Visual Studio Code, so you can write your first prompt.
Prerequisites
To complete the steps in this article, make sure that you have:
An Azure account and access to an Azure subscription. For details on how to set them up, see the pricing page for Azure accounts.
A GitHub account and a GitHub Copilot subscription. For details on how to set them up, see Creating an account on GitHub and Quickstart for GitHub Copilot, respectively.
Visual Studio Code. For details on how to download and install it, see Setting up Visual Studio Code.
The GitHub Copilot extension and the GitHub Copilot Chat extension. For instructions on how to install these extensions, see Set up GitHub Copilot in VS Code and Getting started with GitHub Copilot Chat in VS Code, respectively.
Important
GitHub Copilot isn't included in Visual Studio Subscriptions and is a separate subscription managed by GitHub. For questions regarding GitHub Copilot subscriptions and Support, see Individual Subscriptions or Business subscriptions.
Install GitHub Copilot for Azure Preview
- In Visual Studio Code, select the Extensions icon.
- In the Extensions Marketplace, search for GitHub Copilot for Azure. When the GitHub Copilot for Azure extension appears, select Install.
- If you're prompted, sign in to your Azure account.
Write your first prompt
Ensure that the extension is installed, that you're properly authenticated, and that the extension is working correctly.
If the Chat window isn't already open, make sure it's open by either selecting the Toggle Chat button in the menu bar, or select the dropdown next to the Toggle Chat button and select Open Chat (Ctrl+Alt+I).

In the chat text area at the bottom of the chat pane, enter the following prompt:
@azure Do I have any resources currently running?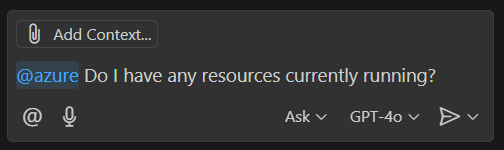
By default, GitHub Copilot uses ask mode. Ask mode provides answers to your prompts in the chat pane. Agent mode enables GitHub Copilot to take action in your workspace.
In ask mode, the @azure part indicates that you want to include the Azure chat participant in the conversation. It scopes your prompt to a specific domain, namely, your Azure account.
The answer to your question depends on what's currently running in Azure in your subscription.
Agent mode
Beginning in Visual Studio Code version 1.99, GitHub Copilot introduced agent mode, an agentic experience that can perform tasks across your entire Visual Studio Code workspace, making edits, executing terminal commands, and so on.
GitHub Copilot for Azure provides "tools" to GitHub copilot to enhance the agentic experience through deep integration with Azure.
In agent mode, you don't need to instruct GitHub Copilot to use GitHub Copilot for Azure with the @azure prefix.
Enable agent mode
You might need to enable agent mode.
In Visual Studio Code, open Settings using the Manage icon (gear).

In the Settings' Search bar, search for
chat.agent.enabled.Check the box next to Chat > Agent: Enabled.

Use agent mode
There are three modes: ask (default), edit and agent. To use agent mode, you must select it in the chat pane.
In the chat pane, in the chat prompt, select the mode dropdown and choose Agent.

The chat pane confirms that you're currently in agent mode.

To see agent mode working, use the following prompt:
What are your tools?The completion response displays a list of GitHub Copilot for Azure specific tools available to GitHub Copilot. The response provides a good overview of the kinds of functionality now available to you:
I can assist you with various tasks using a range of tools. Here are the main tools I have available: 1. Search and Navigation Semantic search for code or documentation File search using glob patterns Text search (grep) List directory contents Read file contents List code usages/references 2. Code Editing and Analysis Insert edits into files Get errors in code files Test search (find test files) 3. Terminal and Git Operations Run commands in terminal Get terminal output Get Git diffs and changed files 4. Project Creation Create new workspaces Get project setup information Install VS Code extensions Create new Jupyter Notebooks 5. Web and API Tools Fetch webpage content Get VS Code API references 6. Azure Tools Azure development best practices Microsoft Learn documentation Azure resource management Azure authentication tools AI model deployment and management Azure Bicep schemas Service configuration and deployment Azure Developer CLI tools Would you like me to explain any specific tool in more detail or help you with a particular task?The last entry,
Azure Developer CLI tools, could be employed with the following prompt:What is the az command to list all my storage accounts ordered by location?The completion to that prompt might generate:
I'll help you generate the Azure CLI command to list all your storage accounts ordered by location. Let me use the Azure CLI generator tool to get the correct syntax for this command. To list all your storage accounts ordered by location in Azure, you can use the following Azure CLI command: az storage account list --query "sort_by(@, &location)" This command will: 1. Retrieve all storage accounts you have access to in your Azure subscription 2. Sort the results based on the location (Azure region) of each storage account 3. Display the full details of each storage account in the sorted order If you'd prefer a more concise output focusing on specific fields, you could modify the query. For example, to show only the name and location in a table format: az storage account list --query "sort_by(@, &location)[].[name,location]" -o table Make sure you're logged into the Azure CLI before running this command. If you're not logged in yet, you can do so with az login.
Enable and disable tools in agent mode
You might want to disable or re-enable certain tools available by GitHub Copilot for Azure.
Select the tool icon in the chat pane.

Use the checkbox next to the list of tools to enable / disable tools (or groups of tools).

Best practices for working in agent mode
To get better agentic results, consider the following best practices.
When prompted, add the
copilot-instructions.mdfile to your workspace.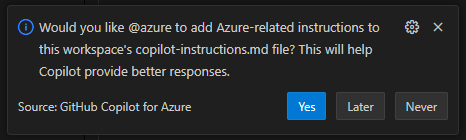
Keep your prompts as granular as possible. Instead of a prompt like
Generate a Python web application and deploy it to Azure, you should break that up into a few prompts each with a smaller scope of responsibility.Allow GitHub Copilot to do work (instead of doing it yourself). Occasionally, GitHub Copilot asks for permission to perform a task with a "Continue" button. While it's possible for you to perform that task outside of the Chat window, you should allow GitHub Copilot to perform the task instead. This allows GitHub Copilot to retain the context of the current state of its larger plan.
Allow GitHub Copilot to repeat itself. Occasionally, GitHub Copilot asks for permission to perform a task repeatedly. It does this to better understand the state of the project files and what it should do next. You should allow GitHub Copilot to repeat tasks it needs to perform.
Express your preferences. If GitHub Copilot wants to perform an action but you would prefer it to take a different action, you can instruct it to do it your preferred way. For example, if it wants to create a folder to contain bicep files called
\.azure, you could intervene and ask it to use a different folder with a prompt such as:Instead of naming the folder `.azure`, please name it `infra`
Optional: Set your default tenant
If you have multiple Microsoft Entra ID tenants, You can set a default tenant using the following prompt:
@azure /changeTenant
Select from a list of your available tenants in the top center drop-down.
You can also set the default tenant in the extension settings:
In Visual Studio Code, on the Activity Bar, select Extensions. Then scroll down to GitHub Copilot for Azure.

Select the gear icon in the corner of the extension's entry, and then select Settings from the pop-up menu.

On the Settings tab, set the Azure Resource Graph tenant to your Microsoft Entra tenant ID. You can find your Microsoft Entra tenant ID in the Azure portal.

Related content
- Understand what GitHub Copilot for Azure Preview is and how it works.
- Follow the quickstart to understand how to include GitHub Copilot for Azure in your software development workflow. The quickstart describes how to deploy services to Azure, monitor their status, and troubleshoot problems.
- See example prompts for learning more about Azure and understanding your Azure account, subscription, and resources.
- See example prompts for designing and developing applications for Azure.
- See example prompts for deploying your application to Azure.
- See example prompts for optimizing your applications in Azure.
- See example prompts for troubleshooting your Azure resources.